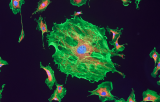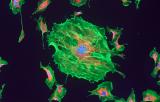
In situ hybridization probes - Pulmonary pathology
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious types of cancer.
Cancer that begins in the lungs is called primary lung cancer. Cancer that spreads to the lungs from another place in the body is known as secondary lung cancer.
There are two main forms of primary lung cancer. These are classified by the type of cells in which the cancer starts growing. They are:
- non-small-cell lung cancer – the most common form, accounting for more than 87% of cases. It can be one of three types: squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma or large-cell carcinoma.
- small-cell lung cancer – a less common form that usually spreads faster than non-small-cell lung cancer.
The vast majority (85%) of cases of lung cancer are due to long-term tobacco smoking. About 10–15% of cases occur in people who have never smoked. These cases are often caused by a combination of genetic factors and exposure to radon gas, asbestos, second-hand smoke, or other forms of air pollution.